
TheĮlectrical infrastructure will rapidly increase in temperature leading toĬomponent failure and even electrical fires. Theīuildings electrical system will be hit by this sudden large demand.

This huge surge in current can cause lots of problems.
#Star delta problem pdf full
When large induction motors start in delta their starting current can be over 5 times higher than the full load current which occurs when the motor stabilises and runs normally.
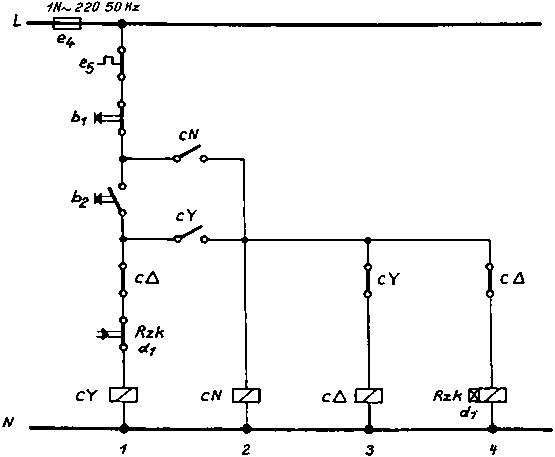
We use star delta which, is also called wye delta in north America, to reduce the inrush current when the motor starts. We always connect the supply side to terminal U1, V1 and W1.įor the motor to run we need to complete the circuit. We’ll see why we do this in just a moment. The coil terminals are in a different arrangement from top to bottom. We have our Phase 1 coil connected to the two U terminals, the Phase 2 coil connected to the two V terminals and the phase 3 coil connected to the two W terminals. Each has a corresponding letter and number U1, V1, W1 and W2, U2 V2. Inside this electrical box we have 6 terminals. On the top or sometimes the side of the motor we have an electrical terminal box. This rotating magnetic field will cause the rotor to spin which we use to drive fans, pumps etc. We then rotate the coils 120 degrees from the one previous to it, then combine these into the motors stator to produce a rotating magnetic field. Intensity and polarity at a different time compared to the other phases. Times compared to the other phases, so the magnetic field will change in In each phase will change direction between forwards and backwards at different Variables into 0–1 variables then a linear interpolation can not be applied to transform (QMKP) into an equivalent 0–1 piecewise linear problem.If we connect each coil to a different phase, the electrons More specifically, we will show that if (III) is used to rewrite the integer Of expansion (III) in the upper bound method. Conversely, we provide the proof of the non applicability We show that expansion (II) providesĪ bound which value is equal to the one computed by Quadri et al (2007).

Namely: (II) a direct expansion with additional constraints and (III) a binary expansion. The use in the upper bound process of the direct expansion (I) employed in Quadri et al. Reduce the number of 0–1 variables so as to make easier the solution to the linearized problem. Suggested by Glover (1975) of the integer variables and in applying a piecewise interpolation to the separable objective function.Īs the direct expansion results in an increase of the size of the problem, other expansions techniques may be utilized to The linearization method consists in using a direct expansion initially This bound is computed by transforming the initial quadratic problem into a 0–1 equivalent piecewise linear formulationĪnd then by establishing the surrogate problem associated. mentioned is the most effective method in the literature concerning (QMKP). To the best of our knowledge the upper bound Is the most appropriate to solve (QMKP) to optimality using the upper bound method proposed by Quadri et al. Our objective is to determine which expansion technique of the integer variables This paper is concerned with the integer quadratic multidimensional knapsack problem (QMKP) where the objective function is separable. The methodology proposed has been successfully tested in SABER simulative environment, before the realization phase measurements on the real converter evidence the correctness of the proposed approach, arising as a general procedure to select a transformer involved in DC/DC conversion strategy, in the context of a boost full bridge topology Read more Finally, the partial results obtained are merged in a conclusive phase, where a single turns ratio have to be chosen due to the bi-directionality of the converter. In particular, the ideal situation is first considered, introducing then a corrective factor for taking into account the dissipative losses due to parasitical effects.

The problem is approached independently first in Buck mode, then in Boost mode. These equations are assumed as the starting point for the core discussion of this paper, about the selection of the transformer turns ratio. Buck) and step-up (or Boost) modulations are then briefly discussed, focusing mainly on the input/output relations in both operative modes. The topological structure is first introduced, outlining the hardware components used. This document aims to describe a rigorous approach to correctly select the optimal turns ratio for a transformer involved in an isolated DC/DC boost full bridge converter realization, considering the input/output voltage ranges, the modulation scheme adopted and the efficiency constraints.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
